Implement an iterator over a binary search tree (BST). Your iterator will be initialized with the root node of a BST.
Calling next() will return the next smallest number in the BST.
Example:
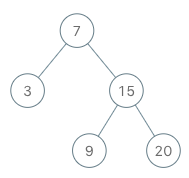
BSTIterator iterator = new BSTIterator(root);
iterator.next(); // return 3
iterator.next(); // return 7
iterator.hasNext(); // return true
iterator.next(); // return 9
iterator.hasNext(); // return true
iterator.next(); // return 15
iterator.hasNext(); // return true
iterator.next(); // return 20
iterator.hasNext(); // return false
Note:
next()andhasNext()should run in average O(1) time and uses O(h) memory, where h is the height of the tree.- You may assume that
next()call will always be valid, that is, there will be at least a next smallest number in the BST whennext()is called.
이 문제는 주어진 BST에서 next함수가 호출 될때마다 BST내에서 제일 작은 값부터 순차적으로 값을 리턴하는 함수를 구현하고, hasNext를 호출했을 경우에는 다음 최소값이 있는지 없는지 여부를 리턴하는 함수를 구현하면 된다.
stack활용하여 dfs같은 방식으로 구현을 한다. BST에서는 한 노드를 중심으로 좌측 자식에는 해당 노드 보다 작은 값을 가진 노드 우측에는 큰값을 가진 노드가 위치 한다.
노드
/ \
작은노드 큰노드
그러므로 항상 작은노드–>노드–>큰노드 식으로 iteration을 하면서 값을 리턴하게 구현한다.
next 함수의 구현은 아래 내용과 같다.
current 노드의 값이 NULL이 아니면 current 노드를 Stack에 push하고 left노드 쪽으로 이동한다. 이것을 계속 반복하다가 current 노드가 NULL 이면 이 loop를 종료한다. 이렇게 되면 현재 stack top에는 출력되지 않은 가장 최소값의 노드(출력 되지 않은 가장 좌측의 노드)가 위치하게 된다.
그리고 stack의 top값을 꺼내서 temp node에 저장한다. temp 노드의 right노드를 current에 저장한다. 그리고 temp->val을 return 하게 되면 next 함수는 항상 출력되지 않은 BST내의 최소값을 return 하게 된다.
결과적으로 next함수를 통해 inorder traversal이 구현된다.
class BSTIterator {
public:
stack <TreeNode*> st;
TreeNode* current;
TreeNode* root;
BSTIterator(TreeNode* root) {
this->root = current = root;
}
/** @return the next smallest number */
int next() {
// current노드가 null이 될때까지 left 노드로
// 이동 한다.
while(current) {
st.push(current);
current = current->left;
}
//현재 스택에 최상단의 값을 꺼낸다.
TreeNode *temp = st.top();
st.pop();
//그 노드의 right 노드를 current에 넣고 현재값을 리턴함.
//right노드가 null이면 위의 while루프를 skip하게 됨으로
//다음 next 함수에서는 현재 temp노드의 상위 노드가 처리된다.
//right 노드가 null이 아닌 경우에는 위의 while loop를 통해
//다음 next 함수에서는 right 노드의 left노드가 처리 되게 된다.
current = temp->right;
return temp->val;
}
/** @return whether we have a next smallest number */
bool hasNext() {
if(current != NULL || st.size() != 0)
return true;
return false;
}
};