Design and implement a data structure for Least Recently Used (LRU) cache. It should support the following operations: get and put.
get(key) - Get the value (will always be positive) of the key if the key exists in the cache, otherwise return -1.
put(key, value) - Set or insert the value if the key is not already present. When the cache reached its capacity, it should invalidate the least recently used item before inserting a new item.
Follow up: Could you do both operations in O(1) time complexity?
Example:
LRUCache cache = new LRUCache( 2 /* capacity */ );
cache.put(1, 1);
cache.put(2, 2);
cache.get(1); // returns 1
cache.put(3, 3); // evicts key 2
cache.get(2); // returns -1 (not found)
cache.put(4, 4); // evicts key 1
cache.get(1); // returns -1 (not found)
cache.get(3); // returns 3
cache.get(4); // returns 4
LRU Cache를 구현하는 문제이다. LRU는 Least Recently Used cache의 약자이다. 제한된 용량의 캐시 영역에서 최근에 억세스된 (put/get 모두의 경우) data가 캐시 영역에 보존 되며. 억세스 빈도가 낮은 순서대로 캐시에 영역에서 제거된다. 이를 이용해서 자주 사용되는 데이터가 메모리 영역에 유지하여 불필요한 로딩 시간을 단축 할수 있게 된다.
구현 방법은 아래 그림과 같이 Doubly-linked list와 Hash map을 활용하여 구현이 가능하다.
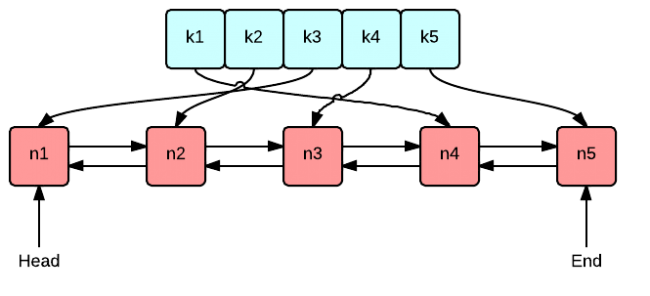
hash map은 주어지는 key값과 linked list의 data의 포지션을 알수 있는 iterator 값을 이용하여 구성된다.
map<int,list<node>::iterator> mp;
list<node> lt;
캐시에 put, get 할 수 있는 두가지 함수를 제공하여 구현한다.
put 함수는 key값을 이용하여 hash map에 이미 해당 키값을 가진 data가 존재하는 확인 후에 이미 존재하면 그 값을 value 파라미터의 값으로 업데이트 하고 list의 splice 함수를 이용하여 리스트의 begin() 위로 이동 시킨다. 그리고 옮겨진 위치를 다시 hash map의 해당 key값에 업데이트 시켜준다.
lt.splice(lt.begin(),lt,itor);
mp[key] = lt.begin();
key값이 hash map에 존재 하지 않을 경우에는 현재 list에 추가된 아이템의 갯수와 현재 캐시의 capacity를 비교 한 후. list의 크기가 capacity 보다 크거나 같을 경우에 만 현재 list의 back()(마지막) 아이템을 삭제한다. 그리고 현재 주어진 key 값과 value로 새로운 노드를 생성하여 list의 제일 앞단에 추가한다. 그리고 list가 추가된 현재 item의 위치를 주어진 key값으로 hash map에 저장한다.
if(lt.size() >= max_capacity) {
mp.erase(lt.back().key);
lt.pop_back();
}
lt.push_front(node(key,value));
mp[key] = lt.begin();
위와 같이 put의 경우에는 put이된 data의 위치를 항상 hash map에 저장하고, 리스트의 최상단으로 위치 시켜서 가장 최근 사용된 순으로 리스트에 존재하게 한다. 그리고 현재 캐시의 내용이 초기에 지정한 용량에 도달 했을 경우에는 가장 사용이 안된 아이템을 삭제하고 새로 put하는 내용이 캐시에 저장되게 한다.
get 함수는 현재 요청한 key값이 hash map에 존재하는지 확인하고, 존재 할 경우 hash map에서 key값으로 list에 key값을 위치를 얻어온다. 해당 key의 data를 가져오고, 현재 key값의 item의 위치를 list의 최상단으로 이동 시킨다. 그리고 그 위치를 hash map에 저장한다.
list<node>::iterator itor = mp[key];
int return_val = itor->data;
lt.splice(lt.begin(),lt,itor);
mp[key] = lt.begin();
전제 소스는 아래와 같다.
using namespace std;
struct node {
int key;
int data;
node* prev;
node* next;
node(int key, int data) {
this->key = key;
this->data = data;
}
};
class LRUCache {
public:
int max_capacity;
int current_capacity = 0;
map<int,list<node>::iterator> mp;
list<node> lt;
LRUCache(int capacity) {
this->max_capacity = capacity;
}
int get(int key) {
if(mp.count(key) != 0){
list<node>::iterator itor = mp[key];
int return_val = itor->data;
lt.splice(lt.begin(),lt,itor);
mp[key] = lt.begin();
return return_val;
} else {
return -1;
}
}
void put(int key, int value) {
if(mp.count(key) != 0){
list<node>::iterator itor = mp[key];
itor->data = value;
lt.splice(lt.begin(),lt,itor);
mp[key] = lt.begin();
} else {
if(lt.size() >= max_capacity) {
mp.erase(lt.back().key);
lt.pop_back();
}
lt.push_front(node(key,value));
mp[key] = lt.begin();
}
}
};